Solar PV
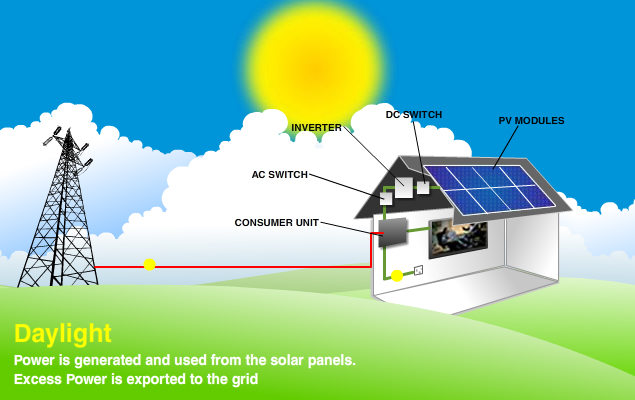
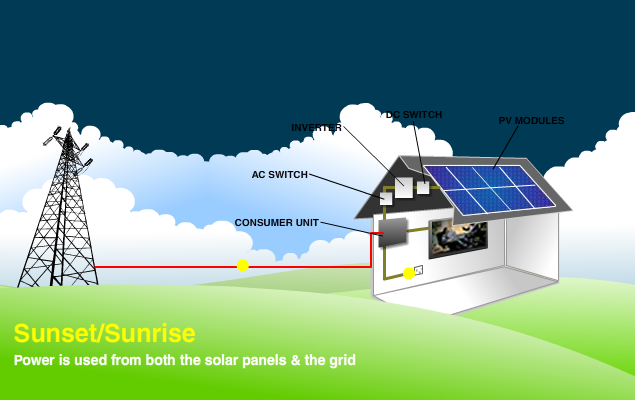
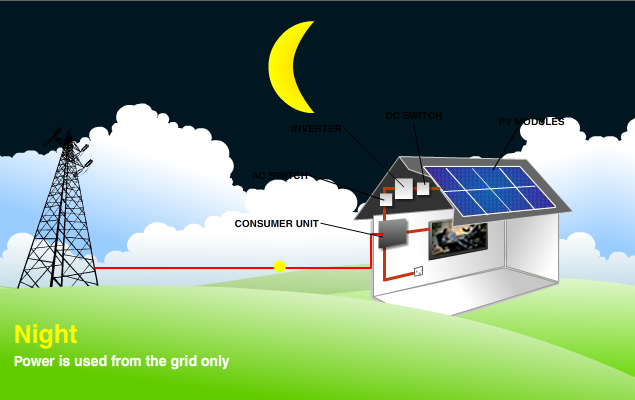
Intro wording here ...Diagram of a Solar PV System
In December 2011 we became an Authorised SunPower Dealer which now gives our customers access to the most efficient MCS accredited solar panel with an efficiency of over 20% ! These panels are not available from everyone, please call for more details.
How does a Solar PV system Work?
 When daylight (solar irradiance) hits the Solar PV panel, electrons are knocked loose from one layer of the panel to the next. This movement of electrons causes an electric current to be generated and with sufficient budget, solar cells and daylight, enough electricity can be generated to run any electric requirements.
When daylight (solar irradiance) hits the Solar PV panel, electrons are knocked loose from one layer of the panel to the next. This movement of electrons causes an electric current to be generated and with sufficient budget, solar cells and daylight, enough electricity can be generated to run any electric requirements.
PV cells do not need direct sunlight to work; electricity can still be generated on a cloudy day.
Solar panels work most efficiently when the light is at 90 degrees to the panel, which is why installing PV panels on an inclined roof surface is preferred.
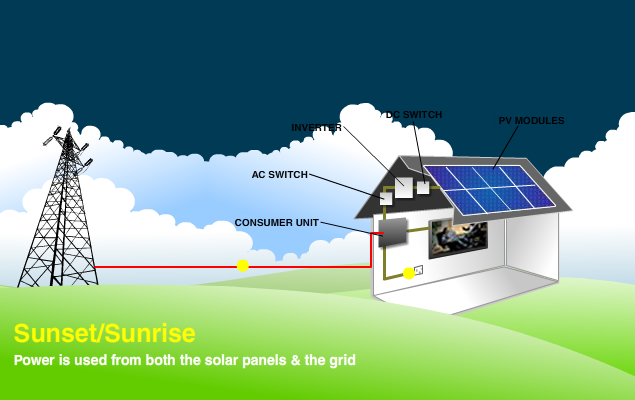
Solar panels produce direct current (DC) electricity, which is the same type of electricity as found in a battery. Electricity supplied from the grid is alternating current (AC) and this is used to power all the appliances and electrical items such as TV’s, computers, household appliances, etc.
In order for the DC electricity to be used by existing electrical items, it must be converted from DC to AC electricity and this requirement is met by the use of an inverter which converts the solar panel DC electricity into AC. The total amount of electricity generated by the system is recorded via a total generation meter.
The electricity generated from the solar panels is used first and any surplus is exported to the grid. Exported electricity can be measured in two ways, either “deemed” (assumes 50% of production is exported) or “measured” via an export meter. In cases where the solar panels are not generating enough electricity to meet the demands (e.g. at night) then electricity from the grid is used.
Grid-connected / Off-grid
There are two main categories of PV systems: grid connected systems which are connected to the electricity grid, and off-grid systems which are not.
Off-grid systems are generally found in areas where there is no connection to the grid. The most common applications are on holiday homes, out-buildings and remote locations. Stand-alone systems are another category of installation where the installation is not attached to a building and not wired to provide electricity to an occupied building. Examples of Stand-alone installations would typically be water pumping installations, boats and transport furniture such as road signs and street lights.
PV module technology and performance
PV cells can be made from different types of materials but the most popular is crystalline silicon. The main types of commercially available cell technologies are:
PV modules
Hybrid and monocrystalline modules are the most efficient panels (between 13-20%) and are slightly more expensive than polycrystalline modules (between 10-15% efficiency). Choosing the most efficient panels means customers maximize the output of the system under different annual weather conditions and less than optimal installation position for the available roof area. Higher efficiency panels also maximize energy production on smaller roof areas.
This ensures maximum financial benefit from the Feed-in-Tariff and the fastest system payback time.
Performance
“At Techfor Energy we aim to achieve the highest performance from our customers’ systems given their requirements”
Cell efficiencies, module efficiencies and system efficiencies can be different. Solar cells when manufactured can achieve an efficiency of 22% (i.e. it converts 22% of the sunlight falling on the surface area of the cells’ surface area into electrical energy).
Module efficiency is less because not all of the module surface area is covered by cells. Also, there are spaces between the cells and the module frame also takes up space. The overall efficiency of the installation is called system efficiency and can be reduced due to voltage drop in cables, inverter choice, shading of the PV modules and many other reasons.
“Achieving the highest performance from our customers’ PV systems means considering both module and system efficiencies”
Techfor Energy supplies the most efficient PV modules, given our clients’ requirements and available budget and we minimize system efficiency losses to ensure the maximum energy output of the PV system.
Customers wishing to invest in PV modules that generate income for 25 years should also consider how long the performance of the system will last. All of the PV modules we select for our clients are guaranteed to perform at 90% of minimum rated power for a period of 10 years and not less than 80% of minimum rated power for 25 years. It is worth noting that PV panels installed in the 1950’s are still producing 80% of their minimum power rating today.
Technology performance is rapidly improving and so at Techfor Energy we regularly review the MCS products database to add new high performance modules to our own products database.
Different types of installations
There are several different ways of installing solar PV products, all of which have a place in satisfying customer and design requirements. They have different costs and efficiencies as well as aesthetic qualities.
Ground Mounted – Tracker System
Like the static ground mounted system in many ways, the tracker system can be installed where roof-based installations are not possible or desirable but these systems have one key difference.
As solar cell efficiencies are maximized when the light hits the panel at 90 degrees, these Tracker based installations seek out and maintain a 90 degree angle between the sun and the panel, through the day and also throughout summer and winter when the relative height of the sun changes.
Through maintaining a 90 degree angle, two-axis Tracker systems increases the productive output & FIT payment income from the same panels by up to 45%. This has the added benefit that it reduces the payback time of the system by 45% also – typically now between 6-9 years, depending upon choice of panel.
This system above all others would maximize energy production and financial return under the FIT Tariff.
Retro-fit
These are the panels that most of us visualize when thinking of Solar panels. They are the most efficient panels and can be fitted to any property which already has a finished roof.
This is the most efficient static installation and maximizes energyproduction and FIT payments.
Roof anchors are fitted to the wooden rafters and rails are then bolted to the roof anchors, with the panels being bolted to the rails.
This type of installation is the most prominent display of your green credentials.
In-Roof/Integrated
These panels are fitted to any property as part of the roof, in place of tiles. The panels are fitted flush with the surrounding roof and are also responsible for waterproofing.
The panels are more expensive and less efficient than retro-fit panels, but suit some aesthetic requirements. For new builds, or extensions, the price of installation can be reduced by not requiring roof tiles for the surface area of the installation.
Air gaps are required behind the panels for cooling, to maintain efficient energy production.
Solar Tiles
These panels are shaped to take the place of 4 typical roof tiles and can be fitted to any property as part of the roof, in place of normal tiles. The panels are fitted flush with the surrounding roof and are also responsible for waterproofing.
The panels are more expensive and less efficient than retro-fit or in-roof panels, but suit some aesthetic requirements.
Like in-roof panels, the price of installation can be reduced for new builds, or extensions by not requiring roof tiles for the surface area of the installation.
Air gaps are required behind the panels for cooling, to maintain efficient energy production
Flat Roof
The existence of only a flat roof to install panels on is catered for by using a mounting system to install conventional retro-fit panels at the optimum angle for the latitude location of installation.
Ground Mounted – Static
Where roof-based installations are not possible or desirable, ground mounted installations are possible. These installations are fitted with vandal & theft proof mountings and an installation base with sufficient ballast below ground to resist calculated wind loads.
What out clients say
Location GU34
So where do you start in a world that you know little about ? For me I had some luck with a recommendation from a friend and called Glenn. From my first conversation it was obvious he has a passion for his job and arranged an initial survey for which he was punctual and very informative. He then produced the survey result and estimate within the agreed timescale. I subsequently accepted and paid my initial deposit (with a little anxiety) but this was unwarranted as everything this company says from Glenn (the owner) to all of his team has been seamless and transparent. Do not look elsewhere !!